The global pruritus (chronic itch) therapeutics market is experiencing a significant transformation. Long relegated to generic antihistamines and topical steroids with limited efficacy for many conditions, the market is now being reshaped by a deeper understanding of itch pathways and the arrival of targeted, systemic therapies. Driven by a high unmet medical need, a growing aging population, and increasing prevalence of underlying conditions like atopic dermatitis and chronic kidney disease, the market is poised for robust growth, attracting substantial investment from pharmaceutical companies.
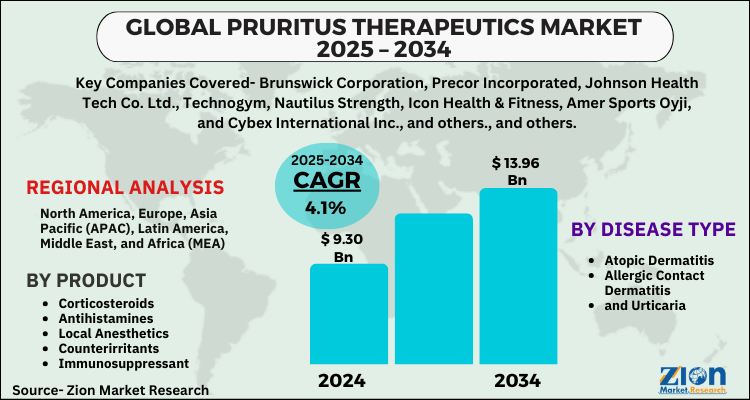
Market Overview and Definition
Pruritus, or chronic itch, is a debilitating symptom associated with over 50 conditions, including dermatological diseases (eczema, psoriasis), systemic disorders (chronic kidney disease, cholestatic liver diseases), and neurological conditions. The pruritus therapeutics market encompasses all pharmaceuticals—topical, oral, and injectable—specifically developed or used to alleviate chronic itch.
The market is segmented by:
-
Therapy Type: Corticosteroids, Antihistamines, Immunosuppressants, Novel Targeted Therapies, Others.
-
Disease Indication: Atopic Dermatitis, Psoriasis, Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD)-Associated Pruritus, Allergic/Contact Dermatitis, Others.
-
Distribution Channel: Hospital Pharmacies, Retail Pharmacies, Online Pharmacies.
Key Market Drivers
-
High Unmet Medical Need: For decades, treatment options were non-specific and often ineffective for moderate-to-severe chronic pruritus, leaving a massive patient population underserved. This gap is the primary engine for new drug development.
-
Rising Disease Prevalence: The global increase in inflammatory skin diseases, particularly atopic dermatitis (eczema), is a major contributor. An aging population also elevates the incidence of conditions like senile pruritus and CKD-associated pruritus (CKD-aP).
-
Scientific & Clinical Breakthroughs: The identification of key itch mediators (e.g., interleukin-31 (IL-31), interleukin-4 (IL-4), interleukin-13 (IL-13), and the JAK-STAT pathway) has revolutionized drug development, enabling precise, biologic, and small-molecule interventions.
-
Successful Market Entrants: The blockbuster success of Dupilumab (Dupixent®), an IL-4/IL-13 inhibitor for atopic dermatitis with profound anti-itch effects, validated the market and demonstrated that payers will reimburse premium-priced, highly effective anti-pruritic drugs.
Current Treatment Landscape and Pipeline Innovations
The landscape is bifurcating between traditional and novel therapies.
-
Established Therapies: Topical corticosteroids, calcineurin inhibitors, and oral antihistamines remain first-line for mild cases. For CKD-aP, gabapentinoids and older drugs like kappa-opioid receptor agonists are used off-label.
-
Novel & Targeted Agents:
-
JAK Inhibitors: Drugs like Upadacitinib (Rinvoq®) and Abrocitinib (Cibinqo®) offer rapid, oral relief for atopic dermatitis-related itch.
-
IL-31 Inhibitors: Nemolizumab, a monoclonal antibody targeting the IL-31 receptor, is a first-in-class agent showing exceptional promise specifically for pruritus in atopic dermatitis and nodular prurigo.
-
Neurokinin-1 Receptor (NK-1R) Antagonists: Serlopitant and tradipitant target the neuronal itch pathway, being investigated for chronic pruritus of various origins.
-
κ-Opioid Receptor Agonists: Difelikefalin (Korsuva®) is the first FDA-approved treatment specifically for CKD-aP, representing a major milestone in disease-specific itch treatment.
-
Market Challenges and Restraints
-
High Cost of Novel Therapies: Biologics and advanced small molecules carry high price tags, creating access barriers and reimbursement hurdles, especially in cost-sensitive markets.
-
Complex Pathophysiology: Itch is mediated by multiple, overlapping pathways. A drug effective for one etiology (e.g., dermatological) may be ineffective for another (e.g., neuropathic), necessitating continued research and personalized treatment approaches.
-
Side Effect Profiles: Systemic immunomodulators carry risks of infections, requiring careful patient monitoring.
-
Persistent Reliance on Generics: For mild or acute itch, inexpensive generic antihistamines and topicals will remain widely used, limiting the addressable market for novel drugs.
Regional Insights
-
North America leads the market, driven by high healthcare spending, rapid adoption of novel therapies, and strong presence of key pharma companies.
-
Europe follows closely, with stringent regulatory frameworks and growing awareness among dermatologists and nephrologists.
-
Asia-Pacific is anticipated to be the fastest-growing region, due to its massive population, increasing healthcare access, rising prevalence of atopic diseases, and improving diagnostic rates.
Future Outlook and Trends (2024-2030+)
-
Precision Medicine in Pruritus: Treatment will become increasingly etiology-driven, with specific biomarkers guiding therapy choice for “itch phenotypes.”
-
Expansion Beyond Dermatology: The most significant growth will come from addressing pruritus in non-dermatological conditions like CKD, primary biliary cholangitis, and hematologic malignancies.
-
Combination Therapies: Using agents with complementary mechanisms (e.g., a biologic with a neurokinin antagonist) to achieve complete itch relief.
-
Emerging Drug Classes: Look for advances in TRP channel inhibitors, PAR2 antagonists, and other neuromodulators targeting the sensory itch nerve fibers directly.
-
Digital Health Integration: Wearable “itch scanners” and AI-powered symptom trackers will be used in clinical trials and, eventually, in treatment management to objectively measure scratch and treatment response.
Read More-
https://www.zionmarketresearch.com/de/report/truck-mounted-concrete-pump-market
https://www.zionmarketresearch.com/de/report/protein-films-market
https://www.zionmarketresearch.com/de/report/bifacial-solar-market
https://www.zionmarketresearch.com/de/report/deep-learning-market
https://www.zionmarketresearch.com/de/report/ultrapure-water-market
Conclusion:
The pruritus therapeutics market has evolved from a stagnant, symptom-focused segment into a dynamic and innovative frontier in medicine. The shift from broad immunosuppression to targeted pathway inhibition is delivering unprecedented relief to patients. While challenges around cost and access remain, the intense R&D focus and robust pipeline ensure that the next decade will see a continued flow of advanced therapies, transforming chronic itch from a neglected symptom into a manageable condition and driving substantial market growth. For investors and pharma companies, this market represents a compelling intersection of clear clinical need and tangible scientific progress.